Introduction
A Dataset is a file that can be opened from a notebook, or which may be an output of a notebook. Common file types include:
TXT - plain text
CSV - comma-separated values
TSV - tab-delimited values
JSON - JavaScript Object Notation, a format to represent a nested data structure
YAML - “yet another markup language”, a variation of JSON that uses indentation instead of curly braces to represent nesting
XML - eXtensible Markup Language, another document-oriented format for nested data structures - popular before JSON
MD - Markup format for representing formatted text
Other - pretty much any file that can be read or written using Python
Importing a dataset
Similarly to notebooks, you can import a dataset by dragging-and-dropping a file onto the Project page. If it doesn’t have an ‘.ipynb’ extension, it will be treated as a dataset.
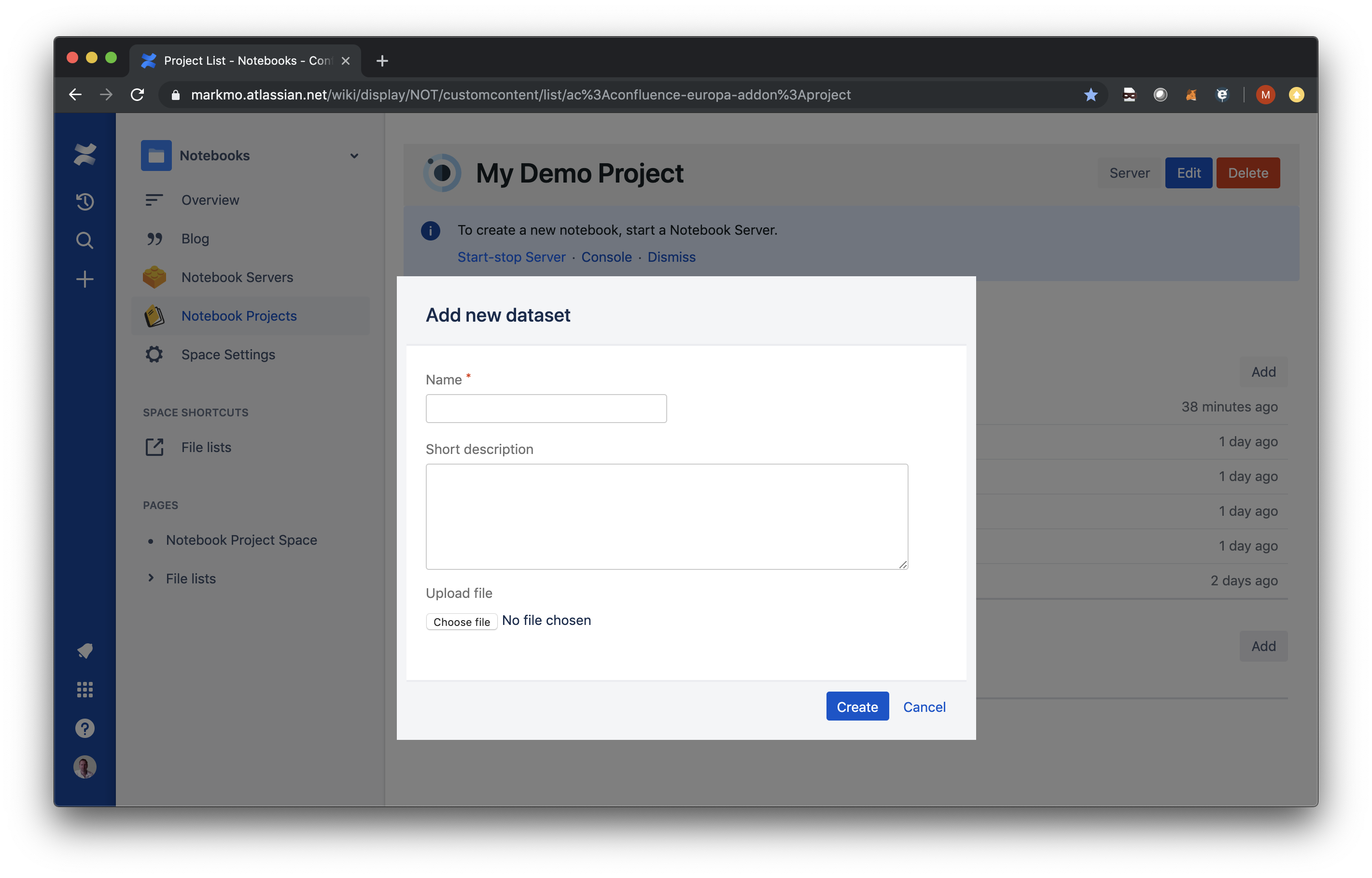
Alternatively, you can use the ‘Add new dataset' dialog, which is opened by clicking on the ‘Add’ button at the top of the Datasets section on the Project page.
Enter an appropriate name and description, and click ‘Choose file’ to select a data file from your local filesystem.
Any data file imported into the system or created from a Europa Notebook is saved to your Atlassian instance. (It is saved as an attachment to the Project.) Europa Notebooks does not persist your data on its servers. A dataset may be read into the memory of a Notebook Server to work on that dataset; however, the Notebook Server is destroyed at the end of your editing session. The only data saved is data written back to Atlassian using the AtlasFS library (Atlas File System).